Complex numbers
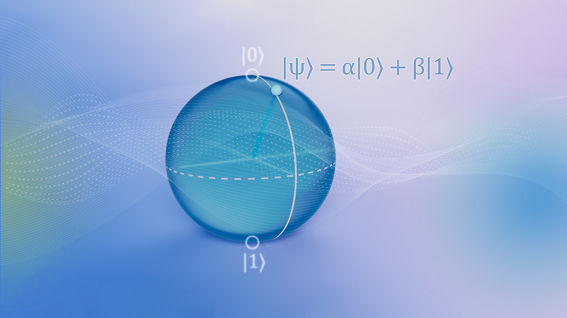
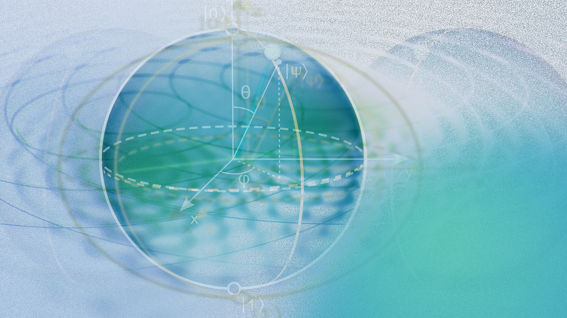
In quantum computing, complex numbers are used to represent the state of qubits and the operations that are performed on them. A qubit is a two-state quantum system that can exist in a superposition of two states simultaneously. Its state is represented by a pair of complex numbers that describe the probability that the qubit will be found in a particular state when a measurement is made. In addition to representing the state of qubits, complex numbers are used to represent the quantum gates that perform operations on qubits. Gates are typically represented by unitary matrices, which are complex matrices that preserve the inner product of vectors. Unitary matrices correspond to rotations and other operations that can be performed on qubits.
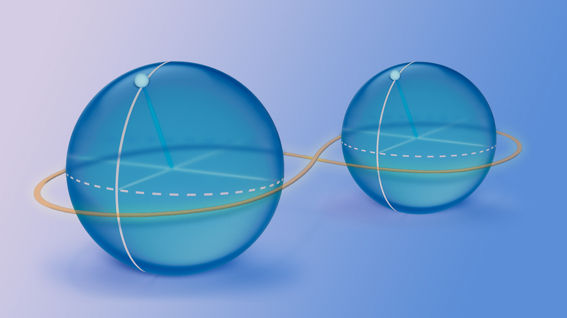
The use of complex numbers allows quantum computing to take advantage of quantum interference and entanglement, which are key features of quantum mechanics. By manipulating the probability amplitudes of qubits using quantum gates, quantum algorithms can perform certain calculations much faster than classical algorithms.
Linear algebra
Linear algebra plays a fundamental role in quantum computing and provides a powerful mathematical framework for understanding the behavior of quantum systems. Quantum systems are described using a mathematical object known as a state vector or a wavefunction, which lives in a high-dimensional vector space. Linear algebra provides the tools necessary to manipulate and analyze these state vectors, which in turn allows us to design and implement quantum algorithms.
Here are some specific examples of how linear algebra is used in quantum computing:
- Quantum gates – the equivalent of classical logic gates – perform operations on qubits such as rotations and phase shifts. Quantum gates can also be used to entangle qubits. These gates are, in fact, unitary operators that act on the state vector of the qubit. Gates are represented as matrices, which are typically 2x2 or 4x4 complex-valued matrices, that must satisfy certain mathematical properties to ensure that they preserve the probability amplitudes of the quantum states.
- Many quantum algorithms, such as Shor's algorithm, use linear algebraic techniques to achieve their computational speedup. For example, Shor's algorithm for factoring large integers relies on the ability to efficiently perform modular exponentiation, which can be formulated as a linear algebra problem involving matrices over a finite field.
- One of the major challenges in building practical quantum computers is the high susceptibility of quantum systems to environmental noise and decoherence. Quantum error-correction is based on linear algebraic techniques and is used to mitigate these effects. Quantum error-correcting matrices act as projectors that can detect and correct errors in the state vector of a quantum system.